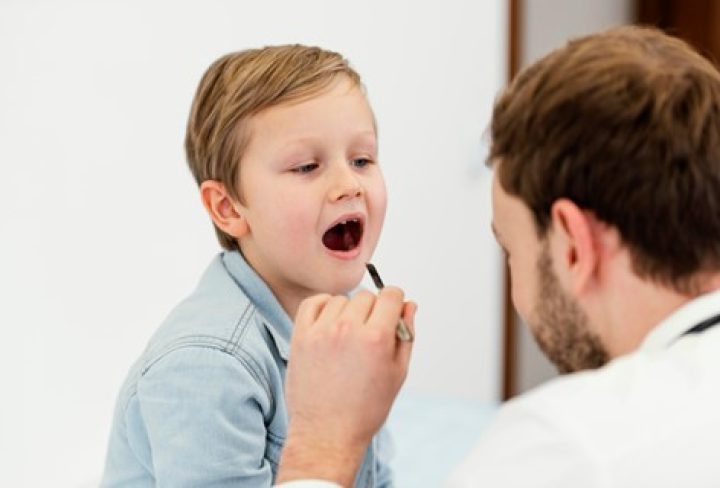
Hand Foot Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a viral infection that predominantly affects infants and young children. While generally mild, it can cause concern among parents due to its contagious nature. This article delves into the intricacies of HFMD, covering its causes, symptoms, available treatments, and preventive measures. By understanding and addressing this condition, parents can ensure their child’s well-being.
Causes of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
HFMD is primarily caused by the Coxsackievirus and Enterovirus families. Transmission occurs through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces. In environments like schools and daycare centers, where children interact closely, the risk of transmission increases, making prevention crucial.
Identifying Symptoms
Recognizing HFMD symptoms is essential for prompt intervention. Common signs in children include:
- Fever: A mild to high fever, often one of the earliest symptoms.
- Sore Throat: Discomfort and pain while swallowing.
- Mouth Sores: Painful blisters on the tongue, inside cheeks, and at the back of the mouth.
- Skin Rash: Red spots or blisters on the palms of hands, soles of feet, and occasionally on knees and elbows.
- Loss of Appetite: Mouth sores can lead to reduced food intake.
Treatment and Management
Although no specific cure exists for HFMD, managing its symptoms is vital:
- Hydration: Encourage fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Pain Relief: Consult a doctor before giving over-the-counter medication for pain and fever relief.
- Rest: Adequate rest aids recovery.
Preventive Measures
Preventing HFMD involves adopting proactive measures:
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly washing hands with soap and water curbs virus transmission.
- Disinfection: Frequent cleaning of touched surfaces, toys, and items minimizes the spread.
- Isolation: Keep infected children away from school or daycare to prevent transmission.
- Limit Close Contact: Avoid sharing utensils and cups to reduce the risk.
HFMD, while common, demands attention and care. Understanding its causes, identifying symptoms, offering supportive treatments, and practicing preventive measures are vital. By doing so, parents can mitigate the impact of HFMD on their child’s health. If HFMD is suspected, consulting a healthcare professional is advised for proper diagnosis and guidance. Keeping your child safe and healthy is a priority, and being informed about HFMD empowers parents to do just that.